Microencapsulation
- Microencapsulation is the process by which tiny liquid droplets or solid particles are suspended or coated with a continuous film of polymeric material.
- Product known as: microcapsules
- Size : micrometer to millimeter (<1mm)
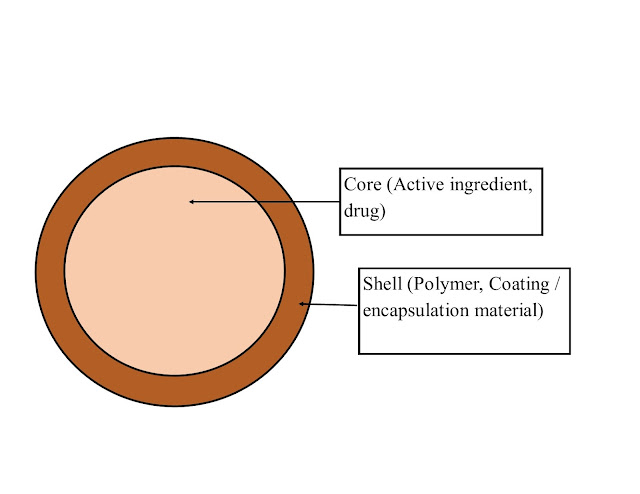
Parts of microcapsules:
1. Intrinsic part (inner): Core: contains active ingredient.
2. Extrinsic part (outer): Shell: comprises polymeric material.
- The shell protects the core from external atmospheres.
- Core material exists in the form of either a solid, liquid and gas.
- Core materials --> solutions, suspensions, emulsions.
- Core material and shell materials should be compatible with each other.
Morphology of microcapsules:
- Mononuclear microcapsules: contain the shell around core.
- polynuclear microcapsules: contain many cores within a shell.
- Matrix microcapsules: core material is evenly distributed inside shell material. i.e. API (drug, core) is dispersed in shell (polymer).
 |
| polynunclear and matrix microcapsules |
Different techniques used for microencapsulation:
Chemical processes: suspension, dispersion and emulsion polymerization, polycondensation.
Physico-chemical processes:
Coacervation, layer-by-layer assembly, sol-gel encapsulation,
Supercritical
CO2 assisted microencapsulation.
Physico-mechanical process:
spray drying, multiple nozzle spraying, fluid-bed coating, centrifugal technique, vacuum encapsulation, electrostatic encapsulation.
Microencapsulation processes with their relative particle size ranges:
|
Microencapsulation
process
|
Size
(micrometer)
|
|
Extrusion
|
250-2500
|
|
Spray-drying
|
5-5000
|
|
Fluid bed
coating
|
20-1500
|
|
Rotating
disc
|
5-1500
|
|
Coacervation
|
2-1200
|
|
Solvent
evaporation
|
0.5-1000
|
|
Phase
separation
|
0.5-1000
|
|
in-situ
polymerisation
|
0.5-1000
|
|
Interfacial
polymerisation
|
0.5-1000
|
|
miniemulsion
|
0.1-0.5
|
|
Sole-gel
encapsulation
|
2-20
|
|
Layer-by-layer
assembly
|
0.02-20
|
|
Class
|
Coating materials
|
|
Water soluble resins
|
Gelatin, gum arabic, starch, polyvinyl
pyrrolidone, carboxymethyl cellulose, hydroxyethyl cellulose, methyl
cellulose, arabinogalactan, polyvinyl alcohol, polyacrylic acid.
|
|
Water insoluble resins
|
Ethylcellulose, polyethylene, polymethacrylate,
polyamide, poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate), cellulose nitrate, silicones,
poly(lactide-co-glycolide)
|
|
Waxes and lipids
|
Paraffin, carnauba, spermaceti, beeswax,
stearic acid, stearyl alcohol, glyceryl stearate.
|
|
Enteric resins
|
Shellac, cellulose acetate phthalate, zein.
|

Comments
Post a Comment