Affinity chromatography
Affinity chromatography is a method of separating biochemical mixture based on a highly specific interaction between antigen and antibody, enzyme and substrate, receptor and ligand, or protein and nucleic acid.
Back in the year of post-graduation, I have delivered a seminar on Affinity Chromatography.
Its Powerpoint presentation is not so good and I did not include much text in the ppt.
Rather I have decided to include only the informative pictures and I explained the whole topic only with those pictures. (I got good grade for this!)
So, here is this ppt. You can download it if you want!
DOWNLOAD
For preparation of this topic I downloaded A Handbook of Affinity Chromatography.
The principle and methods of this chromatography are well explained in this book.
I am giving link of this book for you.
Don't forget to download and read!
DOWNLOAD
Do you know the components of affinity medium?
If not, let's learn about them in short!
Affinity medium is composed of three main components.
1. Matrix:
It is made up of agarose gel.
It serves as an inert matrix to which ligand binds directly or indirectly.
2. Ligand:
Ligand is a component which binds to biomolecules (enzymes, proteins, etc).
This component is specific for each kind of biomolecule.
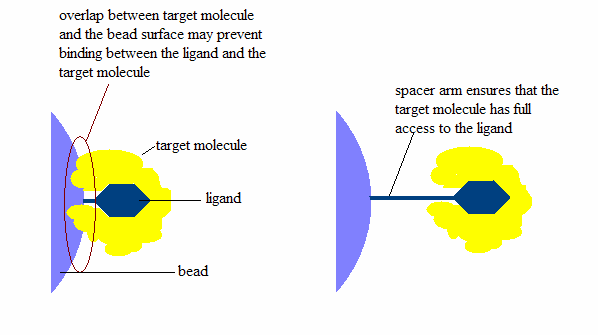
3. Spacer arm:
Binding site is located deep within a molecule.
Spacer arm helps the molecule to bind with ligand.
When binding, length of the spacer arm is an important thing.
Why the length of spacer arm is important?
Importance of length of spacerarm | Source - Wikimedia Commons
The image is self-explanatory, isn't it?
In short, if length of spacer arm is very short, then molecule will not bind properly with ligand.
Ligand will not reach at the binding site of molecule.
If spacer arm is very long, non-specific binding may occur.
For this reason the length of spacer arm should be optimum.
Comments
Post a Comment